참조 문헌
- 曲冠雄, 強磁性体におけるスピンホール効果
- THE SPIN HALL EFFECT IN PLATINUM/FERROMAGNET MULTILAYERS AND ITS APPLICATION
Spin Hall effect는 spin-orbit coupling에 의해 전류의 수직 방향으로 전자의 움직임이 만들어지는 현상으로, 이때 전자가 휘는 방향은 스핀의 polarization에 dependent한다. 이 spin Hall effect를 일으키는 데는 크게 2가지의 현상이 존재하며, extrinsic, 그리고 intrinsic effect로 나누어진다. 또한 extrinsic effect는 다시 두가지 형태로 나뉘어지는데 이는 아래와 같다.
1.1.1. Theory of the spin Hall effect
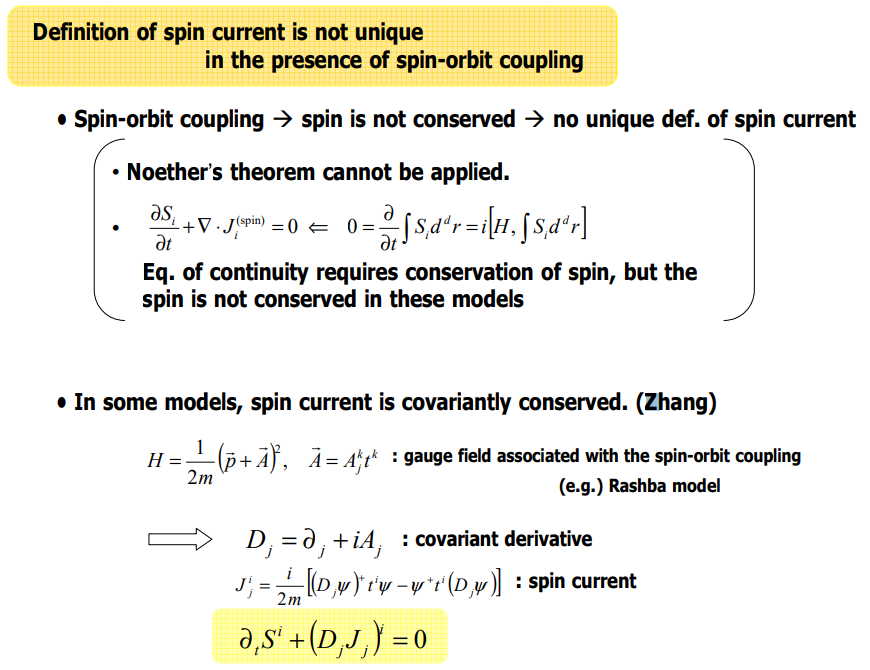
SHE와 AHE는 모두 양자역학적 현상으로, 외부장과 disorder potential에 의해 유도되는 coherent band mixing이 그 원인이 된다. 또 다른 coherent interference 현상과 유사하게, 이 두 현상도 semi-classical Boltzmann 수송 이론으로는 완벽하게 공식화 시킬 수는 없다. 현대의 이론에선, AHE와 SHE 모두 linear response theory를 기반으로 하는 양자역학적 접근법이 적용된다.
AHE와 SHE를 이해하는 이론적 프레임은 크게 3개의 메인 메커니즘으로 분류된다:
- Intrinsic Mechanism (~ band structure of material)
- Skew Scattering Mechanism (~ SOC)
- Side Jump Mechanism (~ SOC)
이 3개의 분류방법은 Bloch state의 transport time $\tau$와 연관되며, 상대적 세기와 물질 purity의 의존성을 통해 구분할 수 있다. 이 분류는 실험적 결과, 그리고 강자성체 물질속에서의 AHE에 대한 microscopic theory를 통해 가능하다.
메탈릭 영역에서는, disorder는 perturbation처럼 작동하고, scattering process는 quasiparticle scattering rate $\tau^{-1}$의 order로 팽창한다.
AHC $\sigma_{xy}$, 또는 SHC $\sigma_{xy}^{s}$의 contribution은 상대적으로 쉽게 확인할 수 있는데, 이는 low order ($\tau^0$, $\tau^1$)로 변하기 때문이다.
AHE와 과련된 실험에서, 이러한 분리는 $\sigma_{xy}$ vs $\sigma_{xx}$ 플로팅을 함으로써 얻어질 수 있으며, 이때 $\tau$는 disorder를 바꿈으로써, 또는 온도를 다르게 함을써 변화된다.
SHE의 경우, spin current는 spin accumulation됨을 통해 측정되어야 하며, 그러므로 측정 방법에 따라 메커니즘을 분리시큰게 상당히 복잡해 질 수도 있다.
It should be noted that several microscopically distinct contributions can share the same $\tau$ dependence. $\tau^1$에 비례하는 contribution은 skew-scattering contribution $sigma_{xy}^{(s),skew}$이며, $\tau^0$에 비례하는 contribution은 두개로 나눠져 intrinsic, 그리고 side jump mechansim이 존재한다.
이 $\tau^0$에 비례하는 side jump와 intrinsic contribution은 dc measurements에 의해서는 실험적으로 구분할 수 없지만, intrinsic contribution $\sigma_{xy}^{(s),int}$를 ac-interand conductivity의 extrapolation을 $\omega \rightarrw 0$의 limt에서 zero frequency로 정의하면 실험적으로, 뿐만 아니라 이론적으로도 이 둘을 분리시킬 수 있다.
이는, 마지막 contribution인 side jump 메커니즘의 정의를 좀 독특하게 만들어주는데, side jump 메커니즘의 conductivity는 아래와 같이 정의할 수 있다.

위의 정의는 일반적으로 semiclassical process에서 나오는 side-jump scattering, 또는 skew scattering과는 관련성이 없으며, AHE와 SHE의 modern linear response에 기반한다.
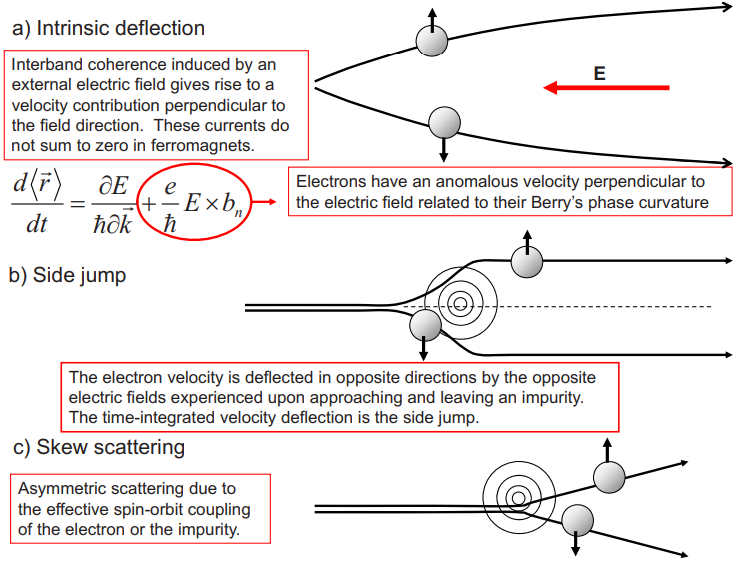
1.1.2. Intrinsic Mechanism
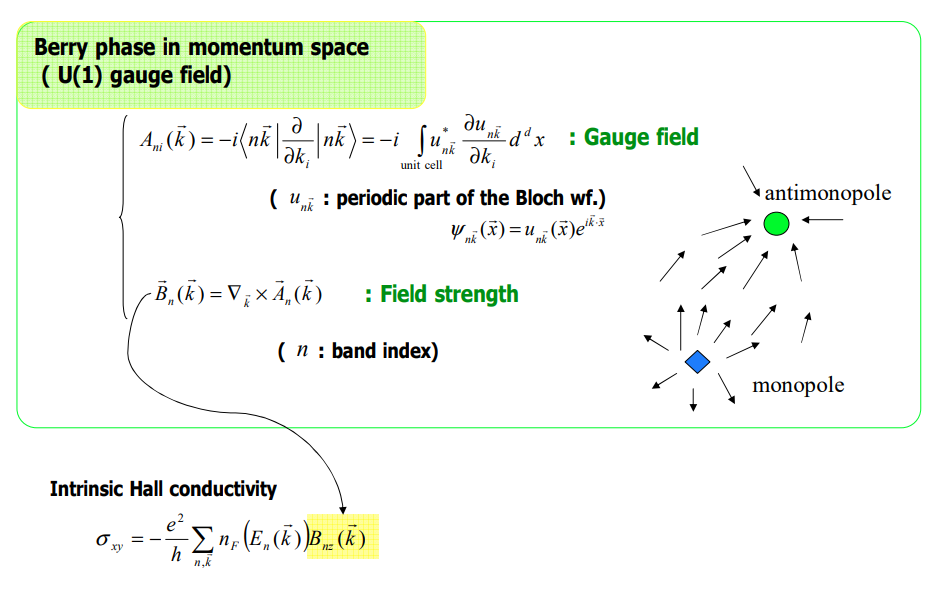
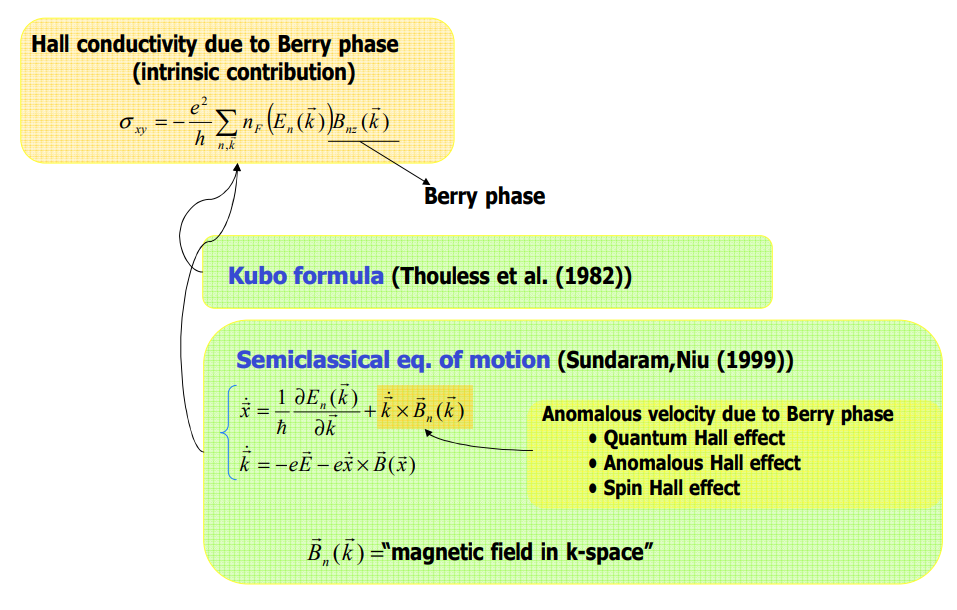
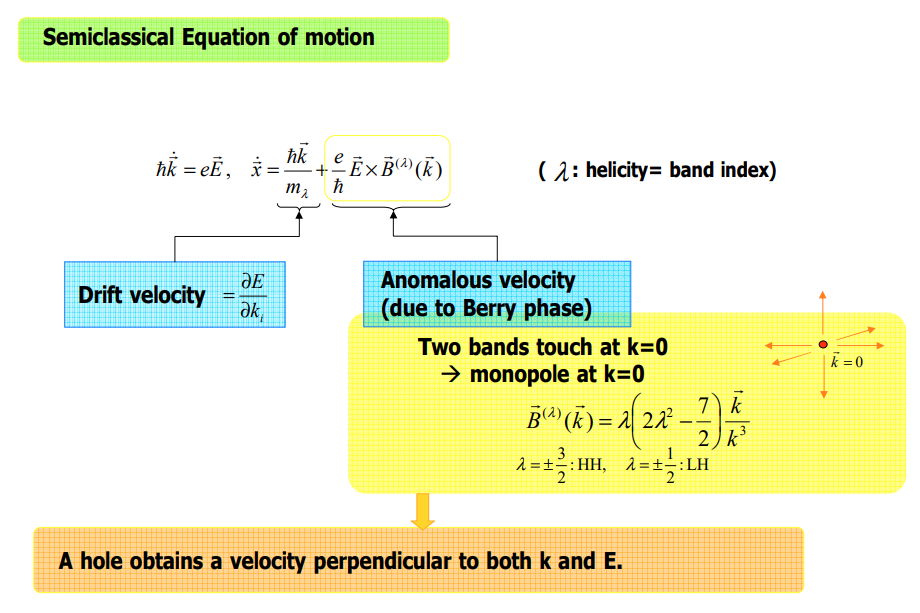
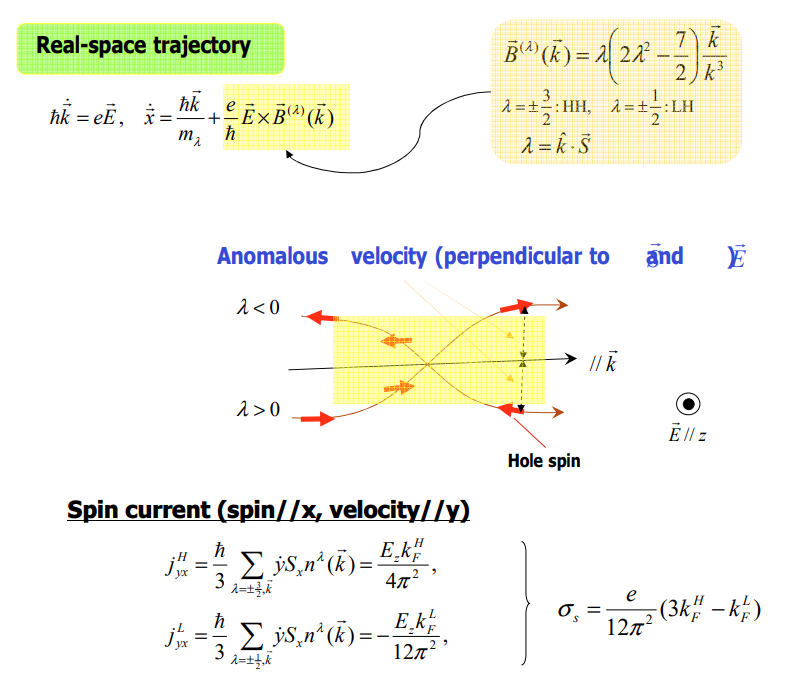
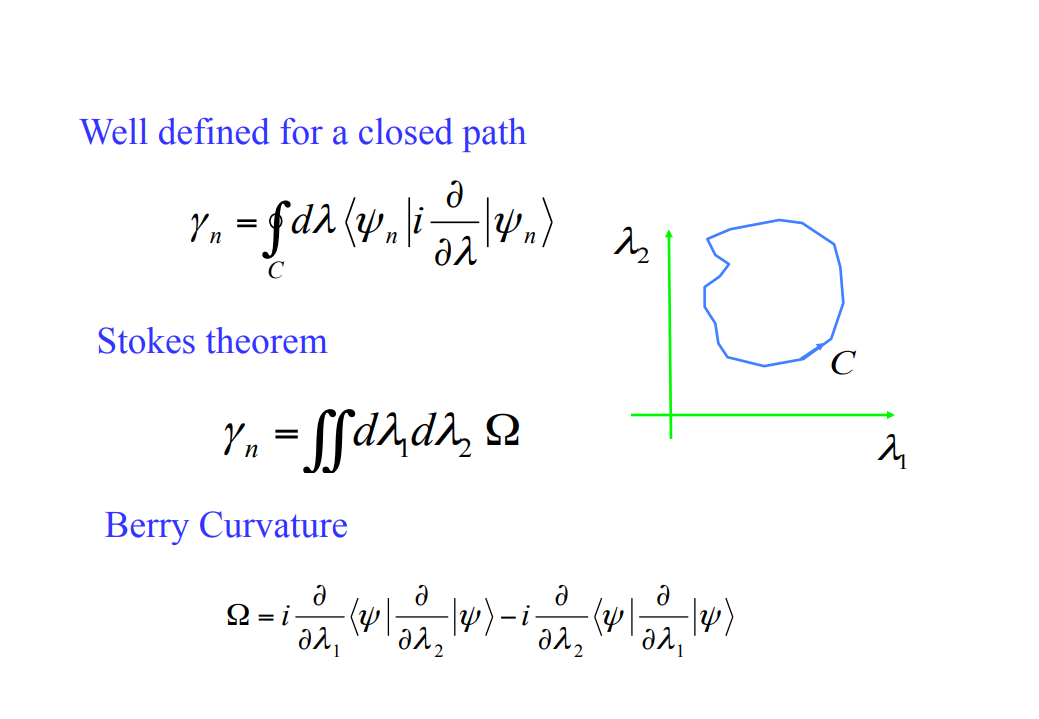
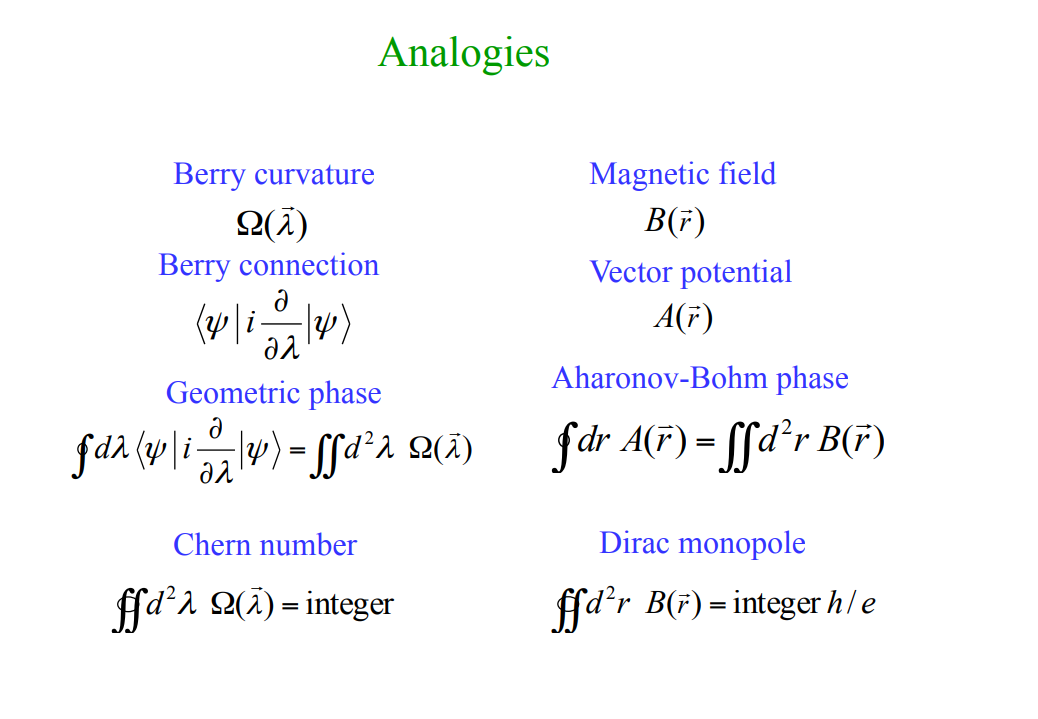
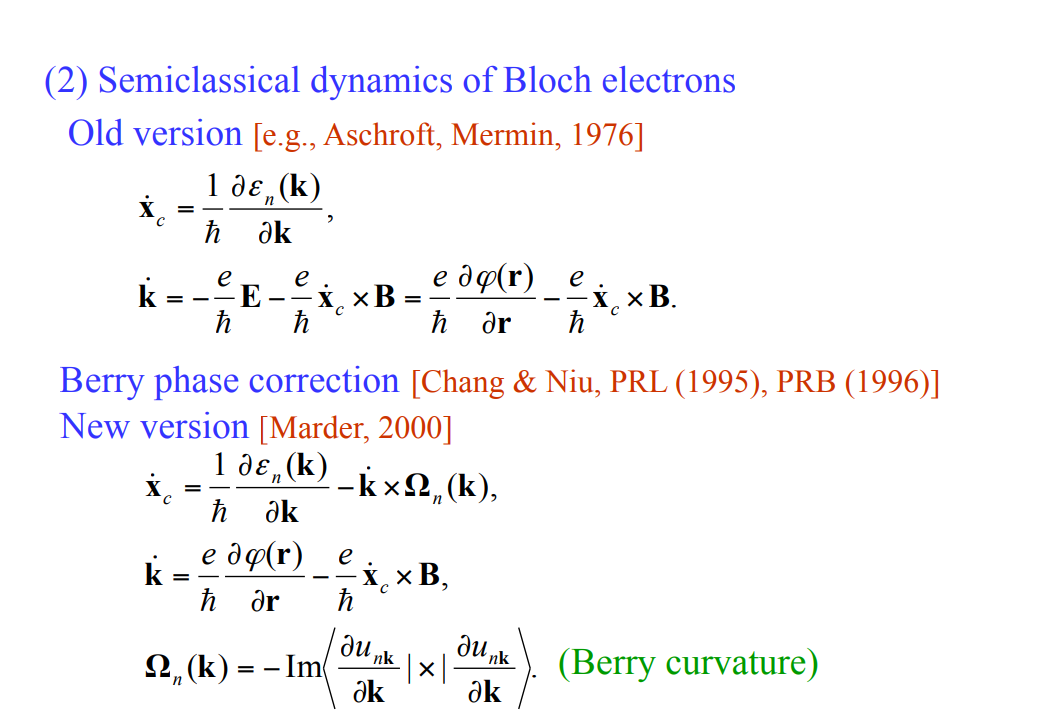
Intrinsic contribution은 3개의 메커니즘 중 값을 정확하게 구하기에 제일 용이하며, 이 contribution이 가지는 topological nature 때문에 이론적 연구에 있어서 가장 흥미로운 주제이기도 하다. Intrinsic mechanism과 semiclassical theory 사이에는 직접적인 연관성 존재하며, 이때 semi classical theory에서는 induced interband coherence가 momentum space에서의 Berry phase로부터 발생하는 anomalous velocity에 의해 확인된다.
AHE에서의 intrinsic contribution은 Karplus에 의해 처음 증명 됐으며, anomalous velocity라 명명 됐지만, 이 topological nature는 최근까지도 완벽히 이해되지는 않았다. Intrinsic AHE에 대한 연구는 강자성 반도체에서의 AHE의 실험적 중요성과 semiclassical transport theory와 momentum-space Berry phase 사이의 간계를 분석하는 것에 의해 동기 부여가 됐다.
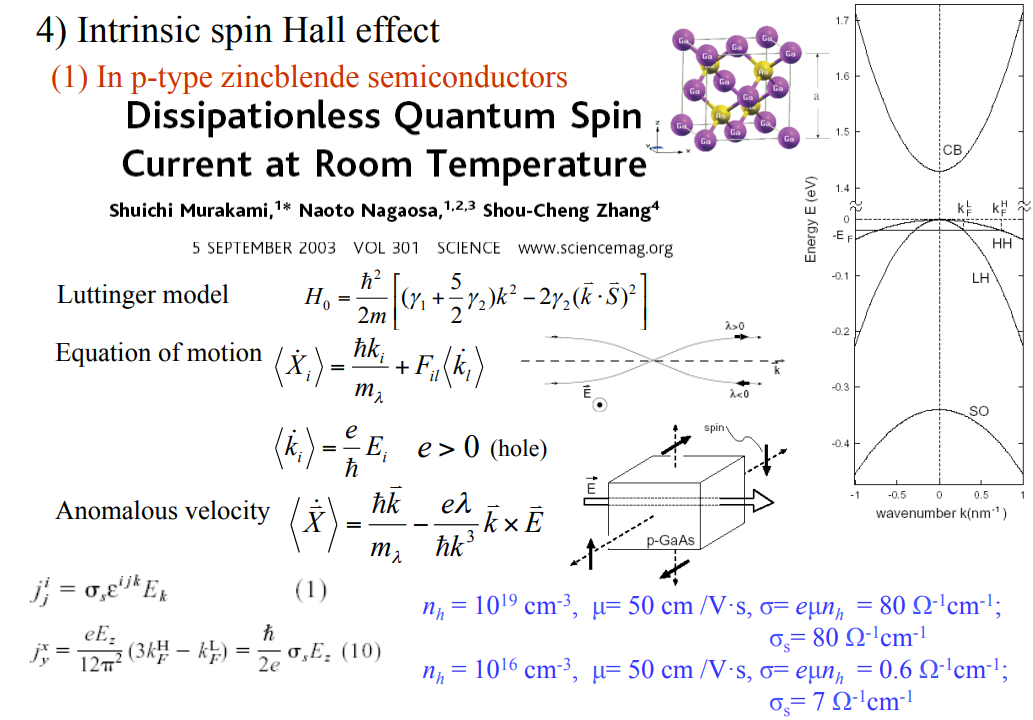
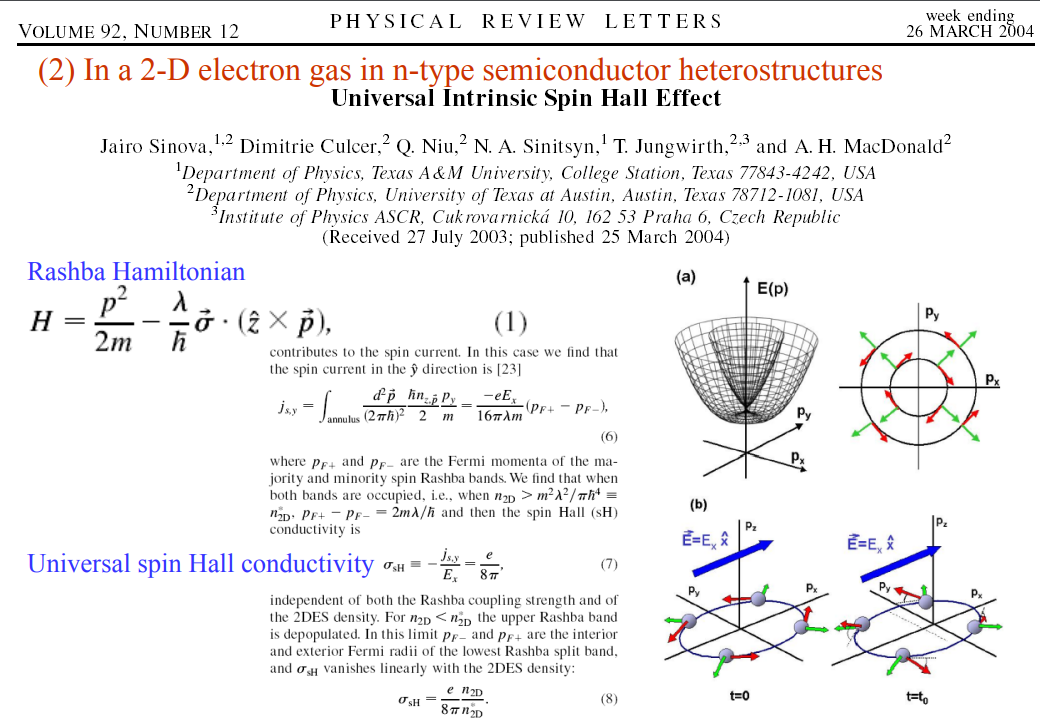
Intrinsic AHE와 유사하게, dissipation이 없는 intrinsic SHE는 Murakami와 Sinova에 의해 처음 제안됐다. [13, 14].
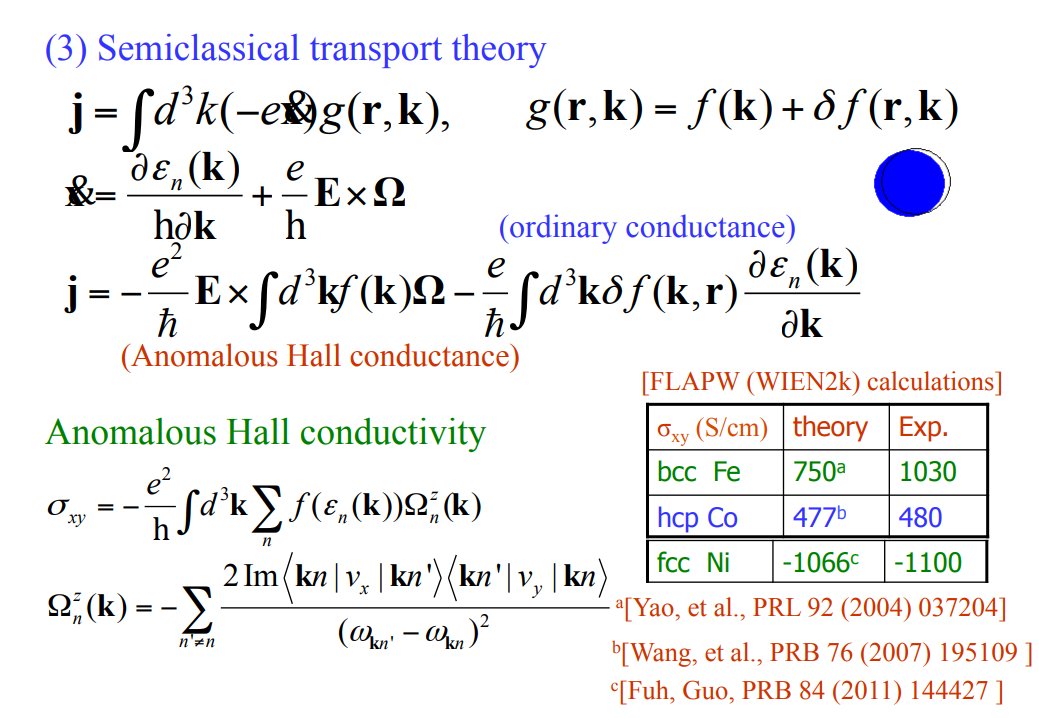
The intrinsic contribution is defined microscopically as the dc limit of the interband conductivity from the Kubo formula for an ideal lattice [14, 28],

위의 식에서 $n$, $n'$은 band indices, $J_i^\alpha$는 $\alpha = 0$인 경우에는 AHE에서의 charge current operator, $\alpha = 1,2,3$인 경우에는 SHE에서의 spin current operator이다. Intrinsic contribution이 더욱이 특별한 이유는, AHE에 특히, Bloch states의 topological 특성과 직접적으로 연결된다는 것이다.
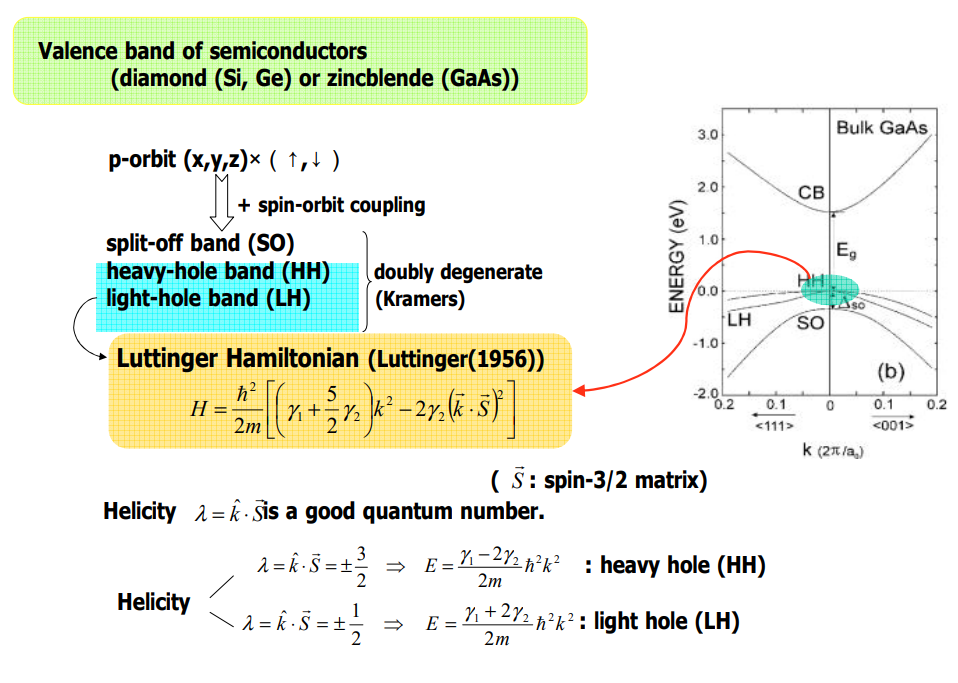
특별히, intrinsic AHE는 각각이 채워진 Berry curvature의 Fermi sea 위에 대한 integration에 비례한단느 것이다. 더욱이, Luttinger model에서의 intrinsic SHE는 또한 heavy-hole bands또는 light-hole bands의 특정한 subspace의 curvature tensor로도 묘사할수 있다. 이는 topological 관점을 드러내 보이는 것이다.
Intrinsic contribution $\sigma_{xy}^{(s),\mathrm{int}}$을 확인하는데 있어 동기 중 하나는, 상대적으로 복잡한 electronic band structure를 가지는 물질이라도, microscopic ab inito 이론 방법을 이용하면 정확하게 계산할수 있다는 것이다. 강력한 SOC bands를 가지는 물질들에서도, intrinsic contribution은 SHE와 AHE를 dominate하는 것으로 보인다.
이 계산법은, 특히 중금속에서, 예상되는 spin Hall angle 값에 대한 semi-정량적인 예측을 해줬다. 계산된 SHC는 전이금속에서 클 것으로 예상되며, Pt와 Ta에서 부호가 바뀔것으로 예상됐으며, 실험적으로도 증명됐다. 이 경우의 spin Hall angle은 아래와 같다.

1.1.3. Skew-scattering mechanism
Skew scattering mechanism은 scattering center가 발생시키는 전기장에 대해 서로 다른 방향의 스핀을 가지는 전자들이 강력한 SOC에 의해 서로 다른 유효자기장을 느끼면서 발생하는 메커니즘이다. SHE와 AHE에서의 skew-scattering은 Bloch state transport time $\tau$에 비례하며, 이로 인해 거의 완벽한 크리스탈 구조에서 우세한 영향을 끼친다.
이 메커니즘은 interband coherence 효과가 일반적으로 무시되는 Boltzmann transport theory에서 SHE, AHE에 영향을 끼치는 contribution이다. (다른 메커니즘들은 Boltzmann transport theory로는 설명이 되지 않음!)
Skew scattering은 SOC의 존재 하에서 disorder scattering을 할 때 나타나는 chiral 특징에 의한 것이다. 이 메커니즘은 Smit 연구팀에 의해 강자성체에서 처음 발견됐고, 상대론적 물리학에서의 Mott scattering으로 부터 근원을 갖는다.
Semiclassical Boltzmann theory에 따르면, skew-scattering contribution은 SOC의 chiral feature로부터 비롯된다. 이 chiral feature는 전이 확률의 left-right symmetry의 균형을 깨뜨린다. SOC가 존재할 때, 완벽한 결정구조, 또는 일부 무질서가 존재하는 경우의 Hamiltonian에서 자화 방향에 상대적으로 right-handed된 전이는 같은 상황에서의 left-handed된 전이와 다른 확률을 갖는다. 전이 확률이 pertubatively 평가 될 때, 비대칭적인 chiral contributions이 3차항으로서 나타난다. 단순한 모델들에서, 운동량 $\vec{k}$, $\vec{k}'$의 전이확률에 대한 비대칭적인 chiral contribution은 아래의 항을 갖는 것으로 종종 나타난다.

여기서 $W_{\vec{k},\vec{k}'}$은 $\vec{k}$에서 $\vec{k}'$으로 전이할 확률이다. Boltzmann 방정식에 이 asymmetry를 추가하는 것은 leads to a current proportional to the longitudinal current
driven by the electric field E and perpendicular to both E and M or σ, where M is the magnetization direction in case of the AHE and σ is the direction of the polarization
of the spin current in case of the SHE.
Skew scattering은 momentum scattering(JC, JS와 모두 관련됨)과 연관되므로, 일반적으로 spin Hall conductivity는 electrical conductivity에 비례하며, spin Hall angle은 electrical conductivity에 무관하다.
Hall conductivity $\sigma_{xy}^{(s),\mathrm{skew}}$와 conductivity $\sigma_{xx}$는 transport lifetime $\tau$와 비례한다. Ab inito 관점에서의 skew scattering에 대한 연구는 Gradhead 연구팀에 의해 시작됐다. 더욱이 ab inito electronic structure와 Pt, Au, Pd 속 불순물(Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni 등..)이 존재하는 시스템에서의 Boltzmann equation을 기반으로 하는 skew scattering에 대한 최근 연구는 수 퍼센티지의 일부분에 대한 spin Hall angle을 구할 수 있었다.
1.1.4. Side jump mechanism
Side jump contribution의 정의는 위에서도 봤듯이 총 AHC(또는 SHC)에서 intrinsic contribution과 skew scattering contribution을 뺌으로써 구할 수 있다. Semiclassical 관점에서의 side-jump contribution은 매우 직관적으로 말할 수 있다: 아래와 같은 Hamiltonian을 가지는 SOC가 존재할 때, 구형태의 불순물로 인한 Gaussian wave packet의 scattering을 생각해보자.

Real space에서의 wave packet의 중심점은 wave vector $\vec{k}$에 수직한 방향으로, 스핀 방향에 따라 비대칭적으로 displacement를 경험하게 된다. 이때 disaplcement는 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.

이러한 종류의 contribution은 Smit 연구팀에 의해 처음 발견됐지만 잊혀졌고, Berger 연구팀이 다시금 재발견 했다. Berger 연구팀은 이 contribution이 AHE의 주요 contribution이라고 주장했다.
SOC가 약한 시스템의 경우, side jump contribution은 disorder potential 내에서의 spin-orbit interaction만 고려하여 계산하여 구할수 있지만, 강력한 SOC가 존재하는 시스템의 경우, side-jump scattering에는 두가지 소스가 존재한다
- The extrinsic side jump: arising from non-spin-orbit coupled wave packet scattered by the disorder potential with SOC.
- The intrinsic side jump: arising from SOC induced aprt of wave packet scattered by the scalar disorder potential (withouht SOC).
위에 언급한 두 contribution 모두 $\tau$에는 무관하며, 다시 말해 실험적으로 intrinsic contribution과 구별하기 힘들다. 하지만, side-jump와 intrinsic contribution은 특정 시스템 파라미터(complex band structure를 가지는 시스템에서 특히)에 대해서 매우 다른 경향성을 보인다. 단순화된 모델에서는 intrinsic contribution과 intrinsic side-jump contribution 사이에 정확한 상쇄가 발생함을 연구를 통해 밝혀졌다(하지만 실제와 가까운 복잡한 모델에서는 위의 일은 거의 발생하지 않는다). 해당 cancellation은 단순화된 시스템 속의 Bloch electron이 가지는 Berry curvature가 단순한 band structure 때문에 $\vec{k}$에 상관 없이 상수를 가지기 때문일 것이다.
Pt의 경우, side-jump contribution이 intrinsic contribution보다 매우 작음이 이론적으로 증명됐다. 그러므로, 남은 도전과제는 intrinsic 과 skew scattering mechansim의 상대적 세기를 평가하는 일일 것이다. Pt 속에서 dominant한 SHE 메커니즘을 확인하는 것은 중요하다. 왜냐하면 Pt의 spin Hall angle $\theta_\mathrm{SH}$($ = \sigma_\mathrm{SH}\cdot \rho$)는 전기적 저항도 $\rho$를 증가시킴에 따라 강화시킬 수 있기 때문이다. 스위칭을 위한 critical spin torque가 주어졌을 때, dissipation energy는 $\rho/\theta_\mathrm{SH}^2=1/(\sigma_\mathrm{SH}^2\cdot\rho$와 같이 스케일링 된다. 그러므로, 아무런 $\sigma_\marhtm{SH}$를 악화시키지 않고 $\rho$를 증가시키는 것은 소비전력을 낮추는 효과를 가져온다.
The thickness dependence of the DL spin torque efficiency of Pt indicates the constant value of SHC, not spin Hall angle.
Intrinsic effect는 이름에서도 알 수 있듯이 외부의 요인(불순물 등)과 상관 없이 에너지 밴드 특성 자체로부터 발생하는 현상이다.
Berry phase에 대한 자세한 설명은 아래의 링크를 통해 확인할 수 있다.
링크 바로가기
2213
There are three mechanisms which are attributed to the spin Hall effect: intrinsic(Berry phase), skew scattering, and side-jump.
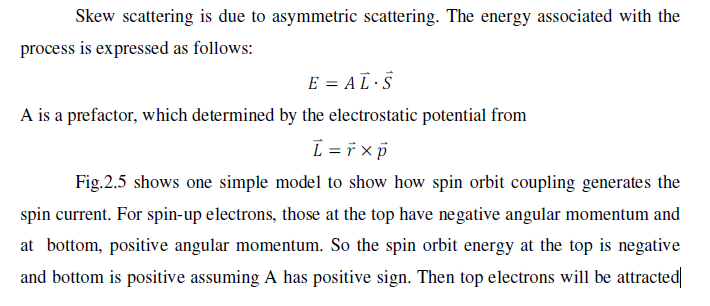
to the atom and the bottom one will be pushed away from the atom. Then both of them
will move on +y direction. Electrons with spin down will move in the –y direction. Thus,
a pure spin current occurs in the y direction when unpolarized beam of electrons is
incident on the atom.
L. Liu et al., Science 336, 555 (2012)

'Spin Hall Effect in Ferromagnets' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Microscopic Picture of the MSHE (0) | 2024.07.31 |
|---|---|
| Interfacial spin-orbit coupling (0) | 2024.04.05 |
| (작성중) Spin Hall effect in Ferromagnets (0) | 2023.04.11 |

댓글